| [栏目图片] |
The Research Team Led by Professor Zhang Xiaojing from the College of Material and Chemical Engineering Publishes Its Latest Findings in the Composites Part B: Engineering |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|||
|
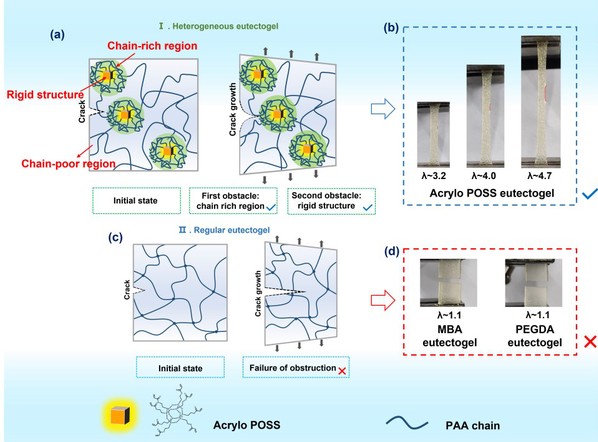
Recently, the research team led by Professor Zhang Xiaojingfrom the College of Material and Chemical Engineering published a research paper titled "A universal strategy for flaw-insensitive nanocomposite eutectogels with centimeter-scale fractocohesive length using multi-crosslinkable polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS)" in Composites Part B: Engineering, a topjournal in the field of composite materials (Chinese Academy of Sciences Q1 TOP journal,IF = 14.2). In this paper, Dr. Fan Kaiqi from the College of Material and Chemical Engineering is listed as the first author, with Professor Zhang Xiaojing asthe corresponding authorand Zhengzhou University of Light Industryas an independent affiliated institution. The paper can be accessed at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2025.113079. To address the critical issue of crack propagation that tends to occur in gel-based soft matters under large deformations, a POSS-basedcompositegel materialcontaining a heterogeneous polymer network was innovatively designed and prepared. This material demonstrated exceptional resistance to crack propagation, with low hysteresis, strong adhesion, andsuperior antifreeze properties (adaptable toa temperature as low as -40°C). The flexible sensors based on this gel exhibited stable strain responses within a wide temperature range, providing an innovativestrategy for developing defect-tolerant and extreme-environment-resistant flexible sensordevices. The team has made a series of significant advancements in the field of flexible functional materials and devices. In the area of energy storage, the team has developed a high-performance flexible supercapacitor designed for extreme environments, with an area specific capacitance of up to 1158.67 mF cm⁻² (at a current density of 0.2 mA cm⁻²). After 2000 charge/discharge cycles, the capacitor maintained more than 95% of its initial capacity. The relevant findings have been published in Journal of Energy Storage (Top Journal, IF = 9.8). The paper can be accessed at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2025.117216.In thefieldof biomedicine, the team has developed a smart gel ultrasound coupling solid patch featuring asymmetric adhesionfunction,effectively addressing the compatibility issues of traditional liquid coupling agents in continuous Doppler monitoring. The research findings have been published in International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (TopJournal, IF = 8.5). The paper can be accessed at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146711. Moreover, the team’s paper "Highly stretchable, self-healing, and adhesive polymeric eutectogel enabled by hydrogen-bond networks for wearable strain sensor," published in Chemical Engineering Journal (Chinese Academy of Sciences Q1 TOP journal, IF = 13.3), has been selected as an ESI Highly Cited Paper. Supported by the National Natural Science Foundationof China, the Natural Science Foundation of HenanProvince, and key programs such as Henan Province Science and Technology Program for Tackling Key Problems, these findings have significantly contributed to the academic advancement of materials science and engineering at our university. |
|
Copyright © 2014 Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, China. All Rights Reserved. Add: No.136 Ke Xue Avenue,Zhengzhou,HenanProvince,PRC. Zip Code:450000 It is recommended that you use IE7 and above version of the browser to visit the web site. |